Brian Choi, Bio-application scientist
For more information, please contact app@parksystems.com
Data Reference: Gordon Jung, Application Scientist
Targeted patch clamping (TPC) is a technique combining patch clamping and scanning ion conductance microscopy (SICM) to guide a pipette to a specific patch-clamping position. The patch clamp is a critical technique for studying excitable cells, such as neurons, cardiomyocites, and muscle fibers, in electrophysiology because it allows the study of single or multiple ion channels in those cells. But it is not possible to use it with small cells or submicron-sized structures in the resolution of the incorporated optical microscope. SICM, however, can identify the cell surface in the submicron scale using the same patch-clamping pipette. In this study, a live ventricular cardiomyocyte cell from a rat was examined by targeted patch clamping using Park SICM. Ion channel signals were successfully recorded at a chosen Z groove location of the ventricular cardiomyocyte.
- Nanoscale pipette positioning on a cell surface based on an SICM image
- Perform patch clamping at a subcellular structure of interest in a single cell
- In tissue (thick and opaque), locate a desirable cell position for patch clamping
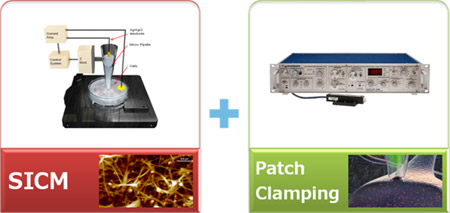 Targeted Patch Clamping
Targeted Patch Clamping
The main idea of targeted patch clamping is to perform patch clamping on small cellular structures in the sub-micron scale detected by SICM. Then, using Park control software (XEP) in SICM imaging mode, high-resolution cell topography is acquired first with a feedback control. Once a suitable structure for patch clamping is identified by SICM imaging, it is approached by the pipette to make a giga-ohm seal, which is positioned by the Z scanner of the ICM. At a certain level, a giga-ohm seal is formed by applying suction. After that, ion channel recording can be performed as in conventional patch clamping.
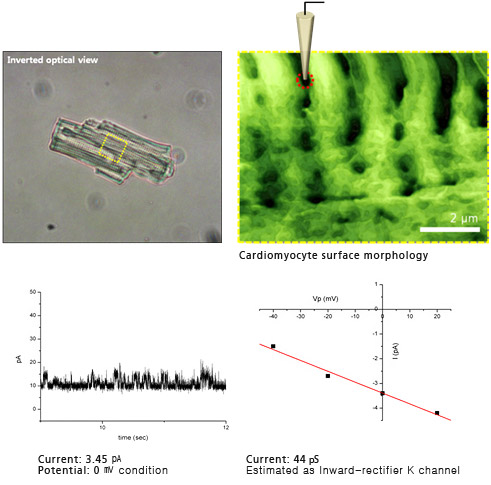 Targeted Patch Clamping on Cardiomyocyte
Targeted Patch Clamping on Cardiomyocyte
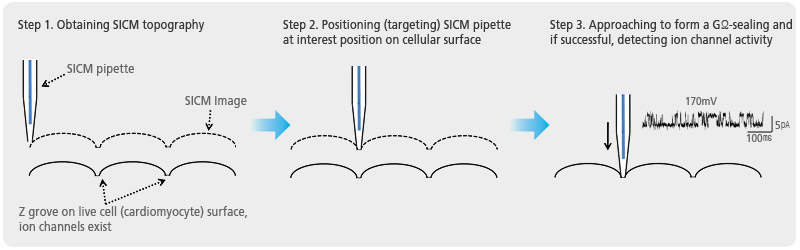 Steps of Targeted Patch Clamping
Steps of Targeted Patch Clamping
Park Cell Analysis Systems
|
|
|
|
| Park NX12-Bio | Park NX10 | Park XE7 | |
| Scanning Ion Conductance Microscopy (SICM) | |||
| Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) with liquid probe hand | |||
| Inverted Optical Microscopy (IOM) | |||
| Live Cell Chamber |